Design of internal control system for government procurement demand management
■ Jiang Aihua Chang Yanzhen
The Measures for the Administration of Government Procurement Demand (Caiku [2021] No.22, hereinafter referred to as the Measures) was formally implemented on July 1, 2021. Among them, risk control runs through the whole process of demand management, which provides a guarantee for the smooth formulation of procurement demand and procurement plan.
This paper takes the government procurement demand management procedure as the main line, combs the risk points of the whole process, and hopes to provide reference ideas for relevant departments or units to improve the internal control system of government procurement demand management and further improve the government procurement demand management system.
General process of demand management
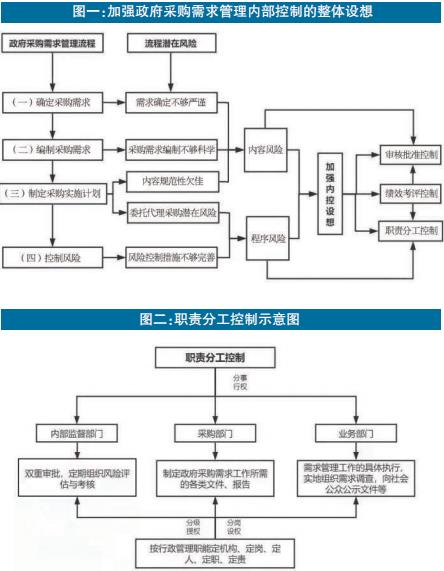
The Measures defines government procurement demand management as: "The purchaser organizes activities to determine procurement demand, prepare procurement implementation plan, and implement relevant risk control management." Accordingly, the author divides the government procurement demand management process into four links: determining procurement demand, compiling procurement demand, making procurement implementation plan and controlling risk.
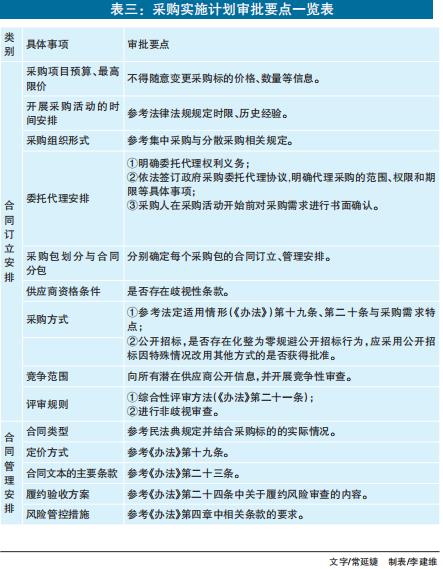
The first step is to determine the purchase demand. Procurement demand is the target that the purchaser needs to purchase and the technical and commercial requirements that he needs to meet in order to achieve the project objectives. Technical requirements are aimed at the function and quality of the procurement target. Business requirements refer to the time, place, financial and service requirements for obtaining the procurement target. Purchasing demand should be carefully determined according to market supply, industrial development, historical purchasing experience and other information. If necessary, it is necessary to carry out demand investigation. According to the "Measures", demand investigation should be carried out for procurement projects in the following four situations: first, procurement projects of goods and services with a price of more than 10 million yuan and procurement projects with a price of more than 30 million yuan; Second, procurement projects involving public interests and high social concern, including public service projects provided by the government to the public; Third, projects with complex technology and strong professionalism, including information construction projects that need to be customized and developed, and projects that purchase imported products; Fourth, other procurement projects that the competent budget unit or purchaser thinks need to carry out demand investigation.
The second step is to prepare the purchase demand. First of all, it should be based on the determined purchasing demand. Secondly, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the project characteristics, actual needs and departmental budget. Finally, we should pay attention to the description of purchasing demand, and the expressions such as words and charts should be accurate and clear.
The third step is to formulate the procurement implementation plan. Procurement implementation plan is the arrangement made by the purchaser to conclude and manage the contract in order to realize the procurement demand. The arrangement for concluding the contract includes the budget (approximate) calculation of the procurement project, the maximum price, the time schedule for carrying out procurement activities, the procurement organization form and the principal-agent arrangement, the division of procurement packages and the subcontracting of contracts, the qualification conditions of suppliers, the procurement method, the scope of competition and the evaluation rules. The contract management arrangement includes contract type, pricing method, main terms of contract text, performance acceptance plan, risk control measures, etc. Usually, according to laws and regulations, government procurement policies and relevant state regulations, combined with the characteristics of procurement demand, financial departments at all levels shall file records in accordance with the principle of simplicity and necessity. In formulating the procurement implementation plan, it is necessary to pay special attention to the risks in the procurement process and contract performance for projects that carry out demand investigation, and put forward targeted risk plans.
The fourth step is to review the key risk items. The Measures clearly stipulate that purchasers should establish a review mechanism to review key risk items in procurement demand management. The review is divided into general review and key review. General review, mainly to review whether the procurement demand is determined and the procurement implementation plan is prepared in accordance with the procedures and contents stipulated in the Measures; Key review refers to non-discriminatory review, competitive review, procurement policy review, performance risk review and other contents that should be reviewed by the purchaser or the competent budget unit on the basis of general review. Projects that carry out demand surveys should be reviewed with emphasis. For projects that fail to pass the examination, the contents of the procurement requirements and procurement implementation plan shall be revised and re-examined.
Main risks in demand management
First, the procurement demand determination link. The risk of determining the demand link is mainly concentrated in the demand survey: first, the projects that need to be investigated according to the regulations have not been investigated; Second, when conducting demand surveys for market participants, the purchasers choose less than three survey objects, which are not representative and violate the provisions of Article 10 of the Measures; Third, according to the actual situation of the procurement project, the demand survey was not carried out in an appropriate way. For example, the opinions of relevant suppliers and experts are not solicited for complex procurement projects, and the opinions of the public are not solicited for public service projects; Fourth, there is no scientific and reasonable price calculation for purchasing demand.
Second, the procurement requirements preparation link. The requirements of the Measures for the preparation of procurement requirements are compliance, completeness and clarity. However, in practice, there may be illegal, incomplete and vague risks in demand preparation, which are mainly reflected in the following four aspects: First, government procurement demand preparation violates laws, regulations and social ethics; Second, the preparation of procurement requirements failed to achieve the specified functions or objectives, and failed to implement the requirements of government procurement policies; Third, the preparation of procurement requirements is incomplete, and the technical and commercial requirements of the procurement target are not specified; Fourth, the procurement demand formulation standards are not compliant, the opinions of relevant suppliers and experts are not solicited, and the factors that may affect suppliers’ quotations and project implementation risks are not fully considered. The indicators are vague and the quantification is unreasonable.
Third, formulate the procurement implementation plan. The risks in the process of making procurement implementation plan can be roughly divided into two categories: procedural risk and content risk.
Procedural risk is mainly the risk in the principal-agent procurement process, that is, the purchaser fails to confirm the procurement requirements formulated by the agency before the procurement activities begin. Content risks mainly include: First, there is no procurement implementation plan; Second, the content of the plan violates the requirements of laws and regulations and does not attach importance to the principles of non-discrimination and competitiveness in procurement. For example, performance requirements are set in violation of the evaluation criteria (suppliers are required to provide samples), or budget standards are exceeded on the grounds of special use, and bulk centralized procurement is avoided.
Fourth, the risk control link. At present, the risk control mechanism of government procurement demand has not yet formed a system, some purchasers’ awareness of risk prevention and control needs to be strengthened, incompatible positions are not set reasonably, and risk prevention and control measures need to be refined. Although the "Measures" clearly put forward to establish a review mechanism, there are still five problems in the specific implementation of some purchasers: First, the review mechanism has not been established according to regulations; Second, there is no review of procurement requirements and procurement implementation plans; Third, the results of the review were shelved, and the procurement items that failed the review were not rectified or re-examined; Fourth, the contents of general review and key review are not comprehensive; Fifth, the demand review post setting does not fully reflect the control mechanism.
Assumption of strengthening internal control of demand management
The fourth chapter of the Measures is "Risk Control", which highlights the importance of internal control system construction in government procurement demand management. According to the process of government procurement demand management and its potential risks, and according to the Measures and the Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Internal Control Management of Government Procurement Activities (Caiku [2016] No.99, hereinafter referred to as the Guiding Opinions), the author tries to put forward some ideas on building a relatively complete internal control system of government procurement demand management and improving the risk control system of government procurement demand management.
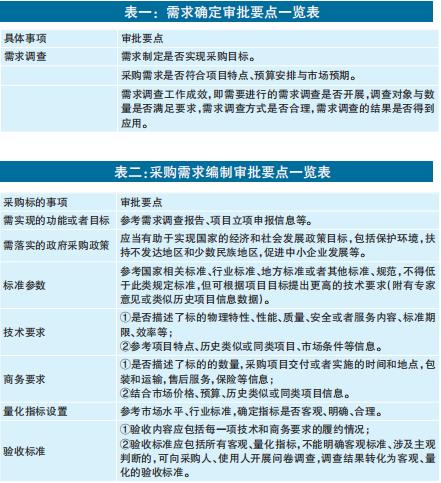
Assumption on internal control system. The Guiding Opinions pointed out that the internal operation and management control system of government procurement should be gradually formed with the main line of "dividing power, setting power in different posts and grading authorization", which is compliant according to law, efficient in operation, controllable in risk and strict in accountability. Based on risk control measures, especially the review mechanism, the author envisages to further build an internal control system, which can be divided into three parts: approval control, performance evaluation and control and division of responsibilities control (Figure 1).
Assumption on the control of division of responsibilities. The control of division of responsibilities is the concrete embodiment of the internal control system of procurement requirements, namely, "exercising power according to different tasks, setting power according to different posts, and grading authorization", and it is also an important measure to contain the risks of procurement requirements management procedures, as shown in Figure 2. It is suggested that units or departments form an internal division of labor system in which internal supervision, procurement and business balance each other, and define institutions, posts, personnel, posts and responsibilities according to administrative functions. Among them, the internal supervision and audit department conducts double examination and approval, and regularly organizes risk assessment and assessment; The procurement department is responsible for formulating all kinds of documents and reports needed for government procurement demand management; The competent business department is responsible for the specific implementation of demand management, organizing demand surveys on the spot, and publicizing documents to the public.
Tentative ideas on examination and approval control. The examination and approval control is mainly designed for the content risks existing in the process of determining the demand, compiling the demand and formulating the procurement implementation plan. It is a further improvement of the examination mechanism to examine whether the content of the procurement demand is legal and compliant (see Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 for the main points of examination). Specifically, the internal supervision department is responsible for the examination and approval control, ensuring that the requirements are set in line with the requirements of laws and regulations and the actual situation of the project, and the final examination and approval personnel need to sign the examination and approval opinion form to realize the responsibility to the people.
Ideas about performance evaluation and control. Performance evaluation and control is mainly designed to strengthen the application of the results of internal control measures, which is mainly reflected in the following aspects: First, it implements "double linkage", linking the internal control system construction, risk assessment and audit results with the performance evaluation of units and departments and the personal development of employees, and mobilizing the positive initiative of units and employees to participate in the internal control system construction. Second, both material incentives and spiritual incentives are given, and appropriate material rewards and praise are given to project team members who have performed well in risk assessment and audit. The third is to intensify punishment and rectification. The audit department should strictly implement the audit system, earnestly perform its supervisory duties, and promptly notify the rectification and review the non-compliant projects. (Author: School of Finance and Taxation, Central University of Finance and Economics)