When I was in college, I had a soft spot for the pet industry. Although I didn’t work in this industry, I still felt that the pet industry had an immeasurable market. The author made a product analysis of the pet-related APP, and this article focused on the understanding and rough analysis of the pet industry.

Recently, I am waiting for new job opportunities, and I have made a shallow analysis of pet-related apps in my spare time. After all, this is an industry that I have been optimistic about since I was in college.
On the one hand, I want to get more job opportunities through my own articles, and on the other hand, I want to communicate with my colleagues. I haven’t worked for a long time, and please correct me if there are any shortcomings in the article (guiding opinions, don’t disturb the bar).
According to the survey statistics of the white paper on the pet industry in China from 2017 to 2019, the number of dogs and cats in cities and towns nationwide reached 99.15 million in 2019, an increase of 8.4% compared with 91.49 million last year, as shown in Figure 1-1; Among them, the number of pet dogs was 55.03 million, an increase of 8.2% over last year; The number of pet cats was 44.12 million, an increase of 8.6% compared with last year.
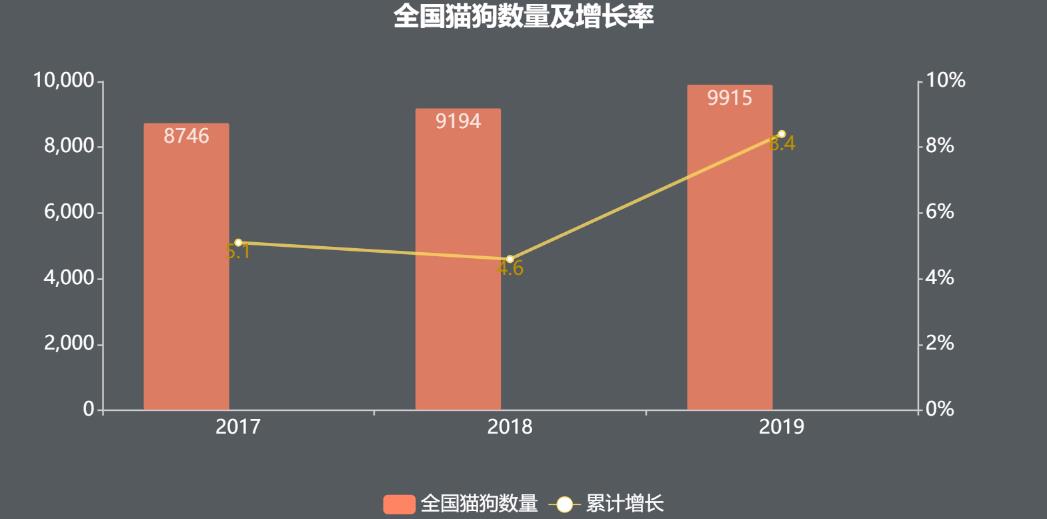
Figure 11 Number and growth rate of dogs and cats in China Source: White Paper on Pet Industry in China.
With the increase in the number of pets such as cats and dogs, the market scale of the pet industry is also expanding rapidly. In 2019, the consumption market scale of urban pet dogs and cats in China reached 202.4 billion yuan, an increase of 18.5% compared with last year, as shown in Figure 1-2. Among them, the consumption market for pet dogs was 124.4 billion yuan, up 17.8% year-on-year, and the consumption market for pet cats was 78 billion yuan, up 19.6% year-on-year.
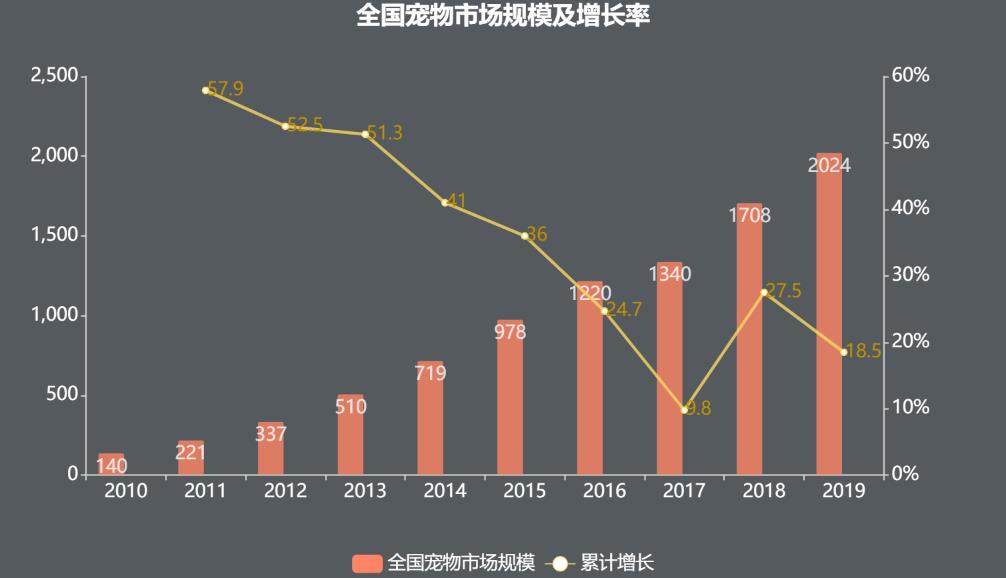
Figure 12 National Pet Market Scale and Growth Rate Source: White Paper on Pet Industry in China.
In the consumption scale of pet market, snacks in pet products and medicines in pet medical care account for the vast proportion and the fastest growth rate. For the purchase of this just-needed commodity, the penetration rate of snacks and medicines is over 70%.
In addition, pet toys and dry food in pet products are also a big expenditure, and the penetration rate of health care products in pet medical care still has a great room for improvement.
Compared with the just-needed consumption, the service consumption is relatively low frequency, and the pet beauty penetration rate is the highest, followed by foster care and pet paradise; However, pet insurance, training, funeral and other consumption are in the "embryonic" stage of the market.
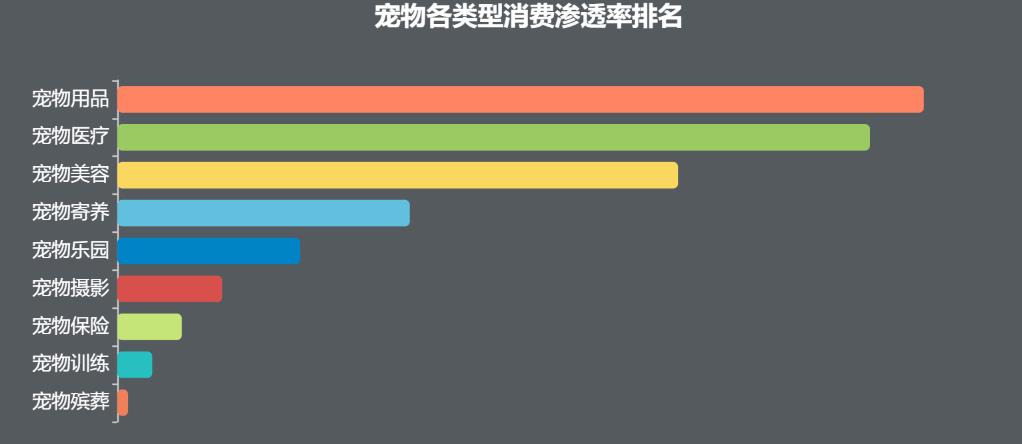
Figure 13 ranking of consumption penetration rate of various types of pets Source: White Paper on Pet Industry in China
Based on the statistical results of the pet market in recent years, it is found that the scale of China’s pet market grew almost linearly from 2010 to 2019, as shown in Figure 1-2. According to the average growth rate (20.0) from 2016 to 2019, the consumption scale of China’s pet market is expected to reach 239.8 billion yuan in 2020, as shown in Figure 1-2.
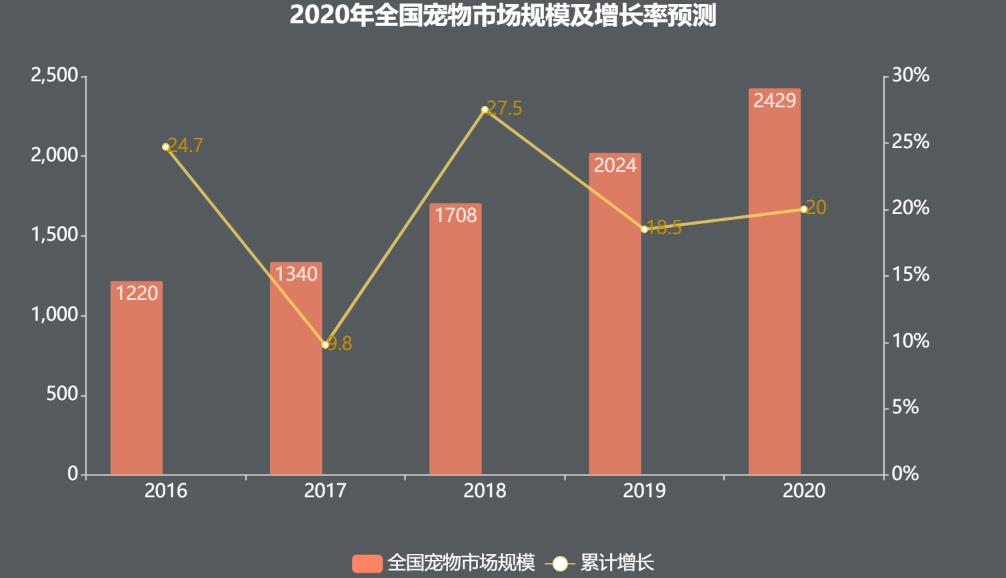
Figure 14 Forecast of the scale and growth rate of the national pet market in 2020.
- In 2020, the number of pet cats and dogs in China will exceed 100 million;
- Every year, the consumption scale of pet market grows steadily, with an average expansion of 5;
- The expansion of the market scale has promoted the rise of pet-type platforms, and it has become an inevitable trend to buy pet necessities online. In addition, it has also promoted the development of new industries such as pet medical treatment, pet grooming, pet foster care, pet training, pet photography, pet insurance and pet funeral.
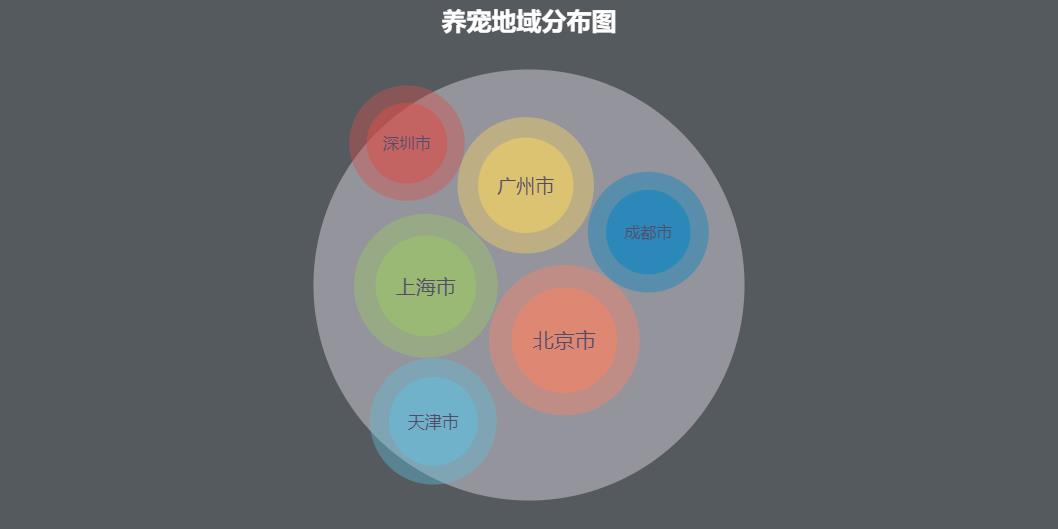
Figure 21 Regional Distribution of Pet Raising Source: White Paper on Pet Industry in China in 2018
As shown in the above figure, the top six cities in the prosperity of pet cities in China are Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Tianjin, Chengdu and Shenzhen.
It can be seen that first-tier cities or quasi-first-tier cities are gathering places for pets. Because these cities are the main inflow places of most migrant workers, the distribution of pets is directly or indirectly related to the overall consumption level, population mobility and educational level of the population.
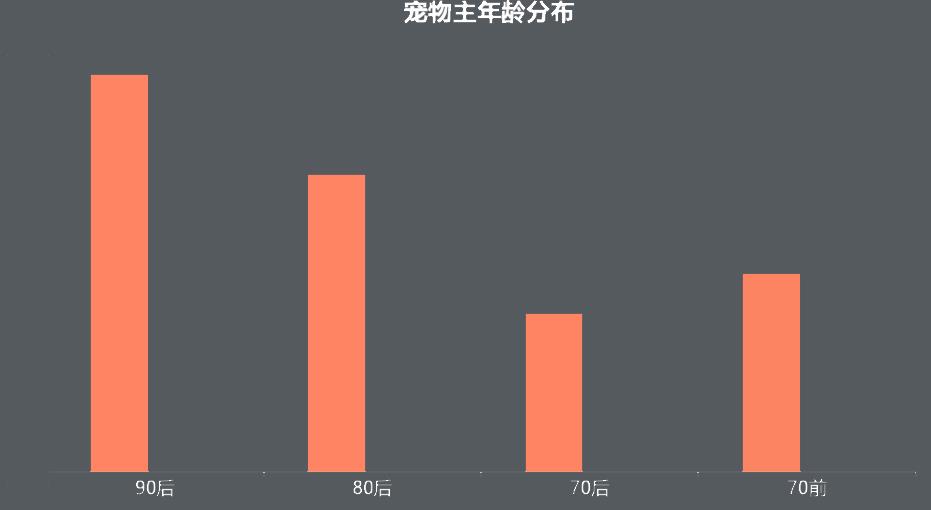
Fig. 22 Age distribution of pet owners
From the above picture, we can see that the post-80s and post-90s are the main force of keeping pets, which shows that keeping pets is gradually becoming younger. Before 70s, most retired people keep pets as companions, while the post-70s prediction may be due to the lack of energy to support the elderly and children to keep another pet.
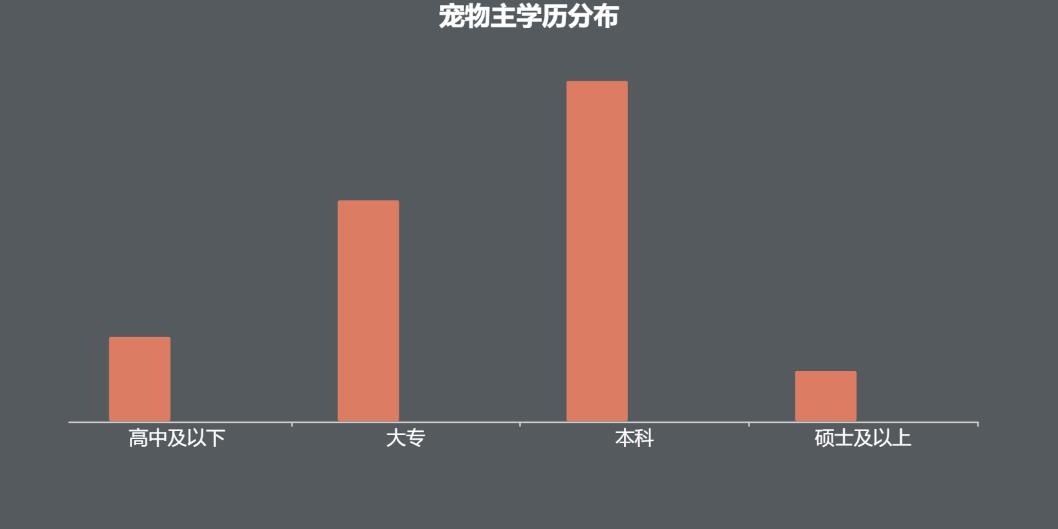
Fig. 23 Distribution of pet master education
In terms of education, pet owners are mainly undergraduate, followed by junior college, high school and below, and finally master and above. It can be seen that pet owners are gradually approaching high education.
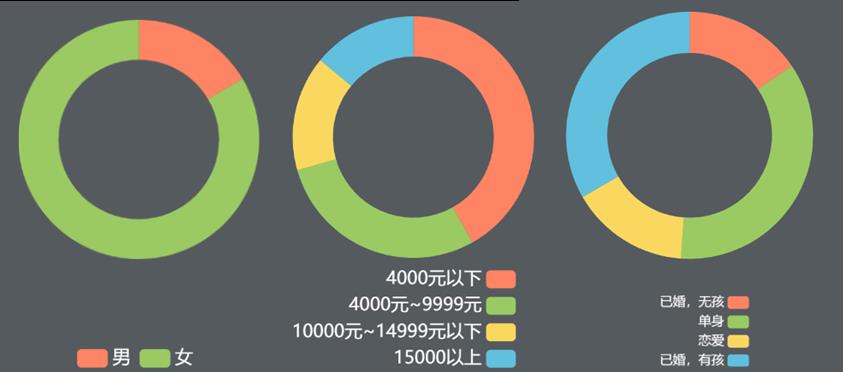
Fig. 24 Distribution of sex, income and marriage of pet owners
In terms of the gender, income and marriage distribution of pet owners, the proportion of female pets is much higher than that of male pets; From the perspective of income, 50.4% of pets earn more than 4,000 yuan, of which more than 20% earn more than 10,000 yuan a month. While pet owners are gradually becoming popular, they are also becoming more and more high-income. As for the marital status of pet owners, single people account for a relatively large proportion, accounting for 32.5%, followed by married families with children, accounting for 28.5%, while married people without children and people in love account for a relatively small proportion.



Through the analysis of the geographical distribution of users and the attributes of users, the user portrait of pet owners is finally obtained.
Divide pet owners into three different groups and substitute them into detailed user scenarios. It is concluded that pet owners are basically for companionship, and they all regard them as their relatives or even children. Because of this, pet owners will take extra care of their pets and are willing to spend time and money to accompany them.
Through the analysis of the current market and users, the pet industry has a very bright prospect and form, so there are many mobile phone apps in generate to cope with the development of the market. Although these mobile apps are all in the pet industry, they are involved in different aspects.
Select 68 pet-related apps from Huawei APP Store, analyze and classify them, as shown in Figure 3-1 below.
Through the introduction and simple trial of these apps, these pet apps can be roughly divided into the following types: pet health, one-stop service, pet mall, door-to-door service, pet breeding, pet socialization, family foster care, pet trading, consultation and sharing, pet news, pet consignment, dog training service, B-end service, intelligent hardware, pet adoption and pet media dating.

Fig. 31 Various types of pet apps
Each type of APP has different emphasis and brings different commercial output value, so the number of similar products of each type of APP is also different. detailed
The number of detailed products of various types is shown in Figure 3-2, and its ranking (as shown in Figure 3-3) is pet mall, pet trading, one-stop service, pet socialization, pet health, intelligent hardware, B-end service, consultation and sharing, pet foster care, pet adoption, pet media dating, door-to-door service, pet breeding, pet consignment and dog training service.

Fig. 32 Schematic diagram of 68 pet-related apps
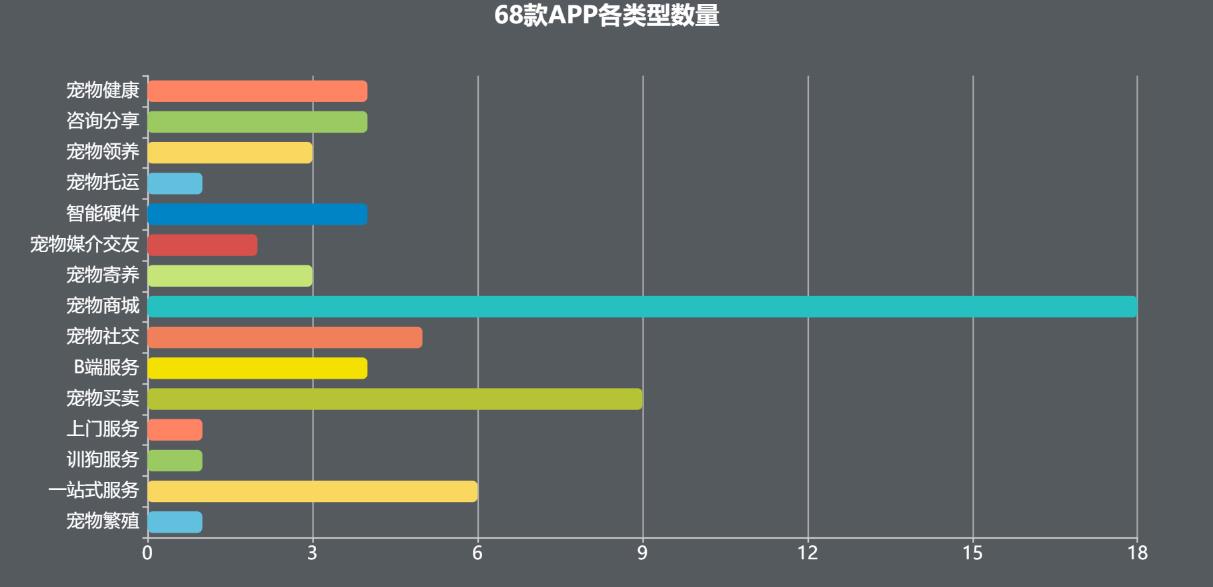
Figure 33 Quantity of 68 APP Types
It can be seen that the type of service that directly conducts online transactions with users is the main positioning of companies for their products, but there are many vertical apps that are avoiding group competition and adopting another way to emerge suddenly.
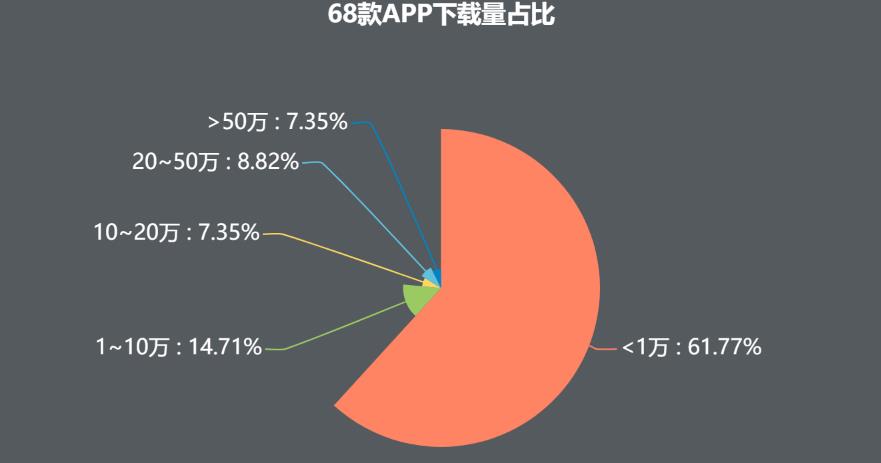
Figure 34 Percentage of downloads of 68 apps
As can be seen from the above figure, most of the downloads of these 68 softwares are not optimistic, accounting for 61.77% of the downloads less than 10,000, and only 7.35% of the downloads more than 500,000, which is not proportional to the number of pet owners. It can be seen that it is far from reaching a stable period in the use of pet mobile terminals.
On the contrary, there is a great market and space to be tapped, and it is in a stage of rapid development.
Select a typical APP from each type of APP as a representative, make a detailed analysis, and finally explore its commercial level from the user level, product level and operation level of the product.
3.3.1 Pet Health-Pet Doctor
1) reasons for choosing
The pet doctor APP focuses on "online consultation of pet doctors". Although its download volume is not the highest in this type, it is more professional than other pet health apps. Everyone’s pet community APP with a relatively high download volume is carried out in the mode of "community+health", and its latest updated version was in October 2017, so the pet doctor APP was chosen as the representative of the pet health type.
2) Business model
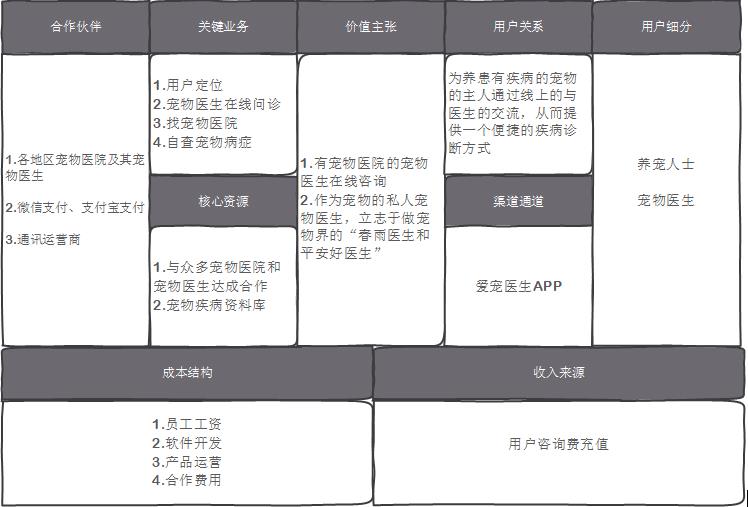
Fig. 35 Canvas of AP business model of pet doctor
This product is a platform for online consultation of pets, which attracts a large number of pet owners to consult about their pets’ diseases by attracting pet doctors from various pet hospitals across the country. When users have consultation needs, they can get points directly through WeChat or Alipay payment, and then choose a doctor they like for consultation.
3) Product function
A. Information architecture
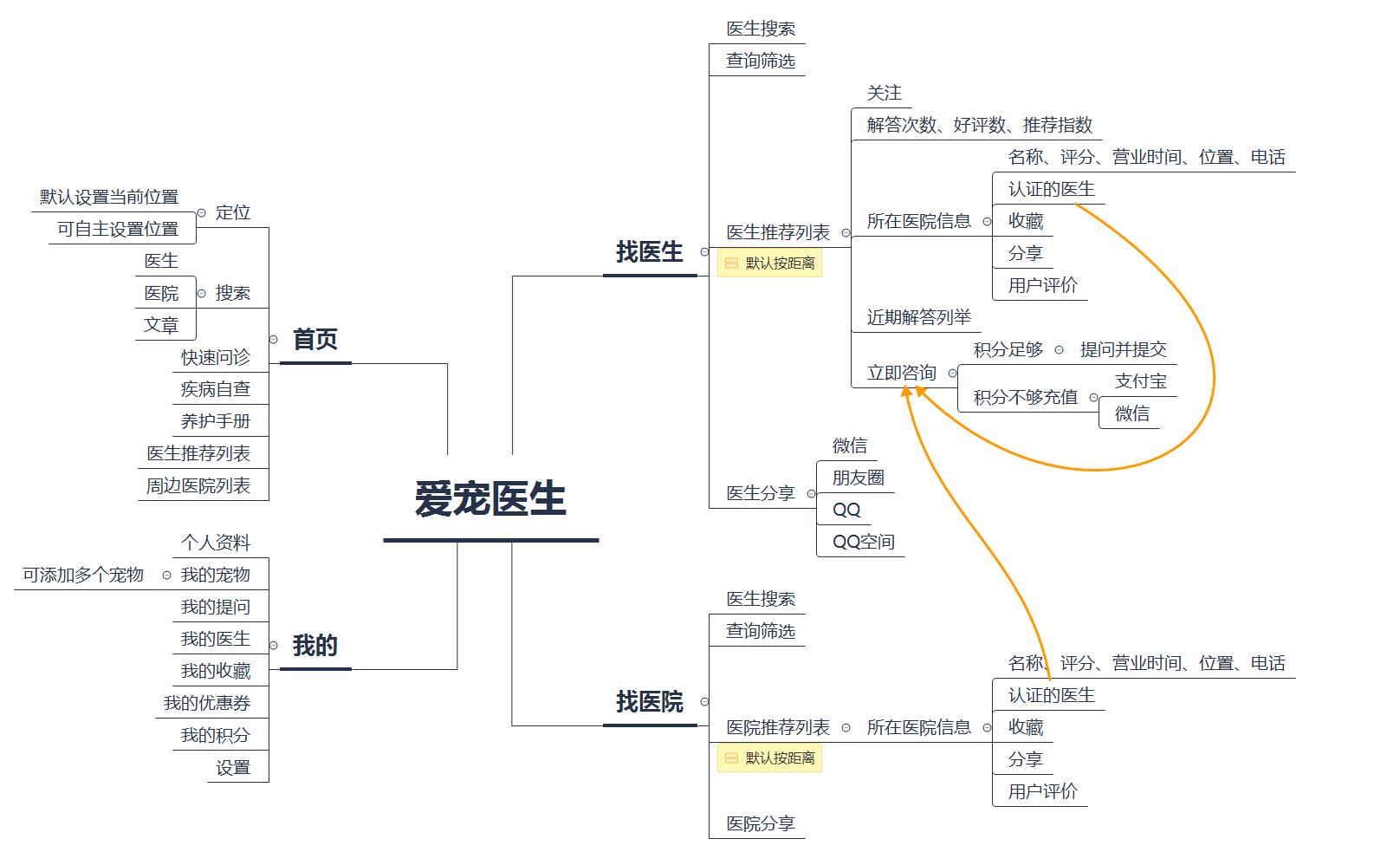
Fig. 36 information architecture of pet doctor APP
The overall information architecture is relatively restrained, and there are not too many complicated functions. The positioning of the four modules is accurate and there is not too much interference information. It is basically based on the core value of the product, "online consultation for pet doctors", and two exciting demand application functions-disease self-examination and maintenance manual are embedded.
B. Process logic
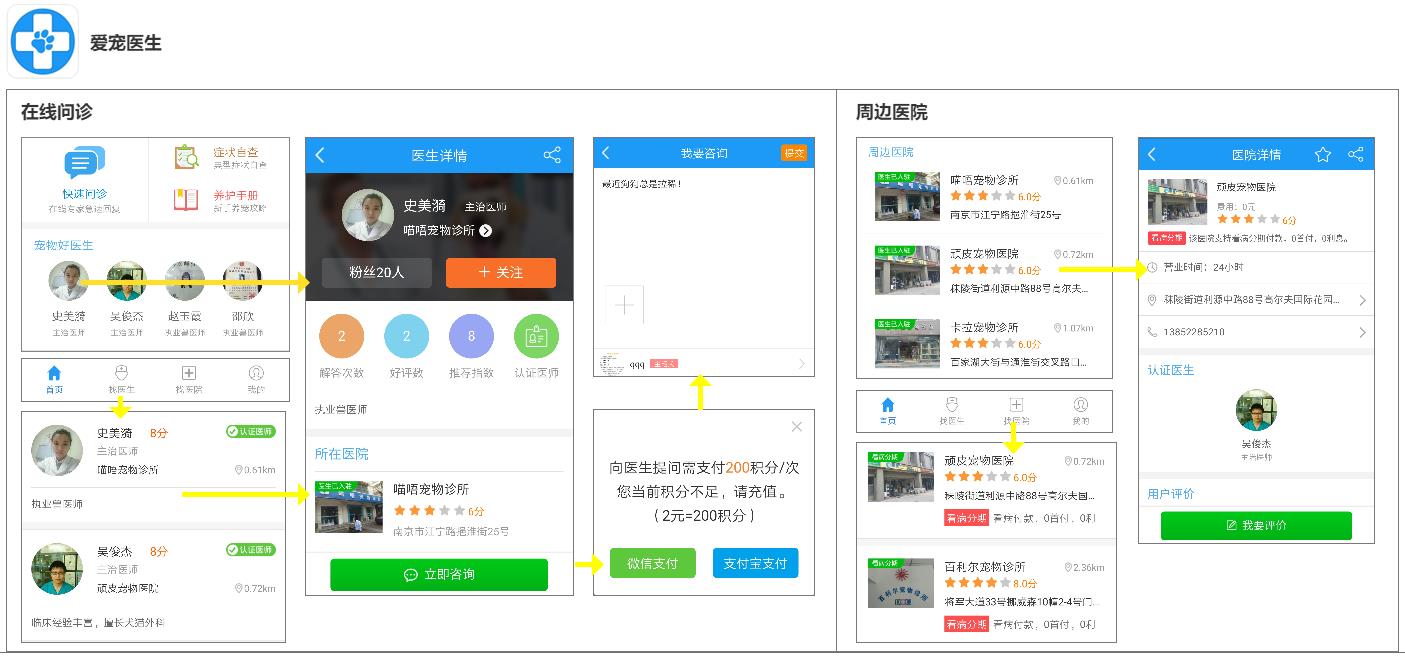
Fig. 37 page flow chart of pet doctor
Users can choose their favorite doctors from the pet doctors recommended on the home page, or they can view a detailed list of doctors in the "Find Doctors" module in the bottom navigation bar. Before consultation, you need to confirm whether the consultation points are sufficient, and you can communicate with the doctor if the points are sufficient.
There are three ways to find a nearby pet hospital. The first way is to look at the hospital recommended on the homepage, the second way is to click "Looking for a Hospital" in the bottom navigation bar, and the third way is to look at the hospital where you have entered the details of a pet doctor.
4) Operation strategy
A. Operating mode

Figure 38 Operation mode
At present, the product operates with coupons and integral mall, as shown above.
In terms of user growth, every user invited to register will receive 200 points. It is suggested to add a function of sharing to get points. Another one can increase the membership system, invite a user to register and get a 30-day free membership, and the member enjoys unique membership rights (medical treatment by stages, consultation discount, etc.).
It is suggested that new users can get a free consultation opportunity after registering, so as to experience the whole online consultation process for themselves. The specific process can be that after registering and logging in, the user can make a selection lottery (consultation coupon/fixed hospital designated doctor consultation) to get consultation discount.
B. Version iteration
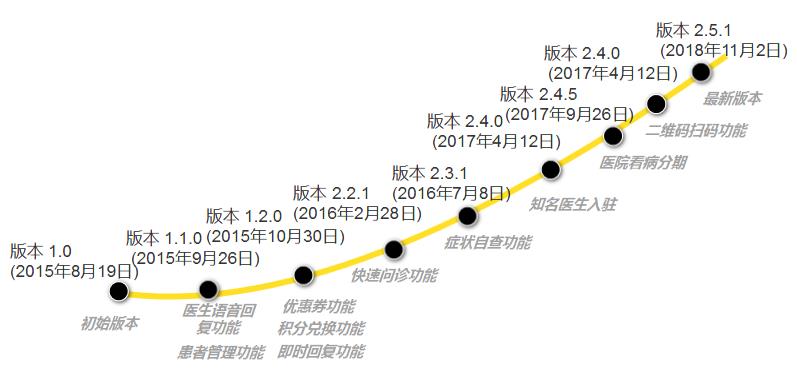
Figure 39 iteration of pet doctor APP version
Doctor Ai Chong APP was created by Shanghai Chong Ling Network Technology Co., Ltd., which was registered on June 15, 2015 with a registered capital of RMB 163,776 million. As can be seen from Figure 3-9 above, the first version of Doctor Ai Chong APP was launched on August 19, 2015, so this product is the first product promoted by this company. According to the frequent version iterations since then, it can be seen that this is also a main product.
After improving the doctor’s online consultation service, this product gradually increases other exciting needs (symptom self-examination function, etc.), and slowly develops online and offline services (hospital treatment by stages, etc.). In this case, the product wants to specialize in pet medical care, strive to be in-depth and professional, and take the development goal of large-scale pet medical care.
It is predicted that the business with offline hospitals may increase in the future, such as listing what services a pet hospital can provide to pets, and users can place orders at the terminal themselves and then go to the store to serve; Continue to improve the online consultation with the pet doctor, you can collect the pet doctor to give an in-depth explanation (article form/video form) on a pet’s disease, and then the user can read and download the video or article by using the form of point redemption.
5) Summary
As a professional online pet consultation APP, the core of pet doctor is to meet the needs of pet owners and resident pet doctors for paid consultation, but the operation mode of this business needs to be strengthened, such as doctors’ professionalism (qualifications, expertise, certificates, etc.), discounts for new users, and strengthening the business line of offline hospital stores (medical appointments, etc.).
3.3.2 Pet Mall-Boqi Pet
1) reasons for choosing
Boqi Pet is a pet store APP developed by Boqii for pet lovers and families. It has selected tens of thousands of pet necessities for dogs, cats and aquarium, covering cat food, dog food, fish, shrimp and turtle food, pet snack toys, daily pet care, pet health care, pet supplies and so on.
Boqi Pet is the most typical and the most downloaded one in the pet mall, and it is also the most downloaded one among the 68 softwares. Its PC-side Boqii was launched as early as 2008, and it is the leader in the industry (as shown in Figure 3-10), posing as a comprehensive service pet website.
The company’s slogan is "Pochi takes care of pet life in an all-round way", so its mobile phone only launched the first edition in 2018 on the basis of the number of users sitting on the portal, and it can have 3.84 million users in just one year, which shows that its development trend is also very fast.
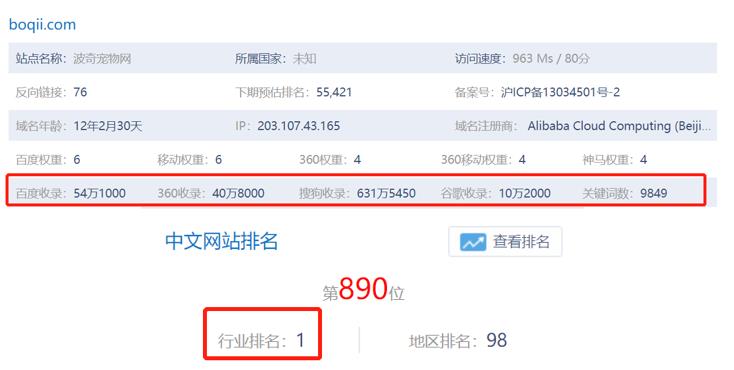
Figure 310 Industry Ranking Chart
2) Business model
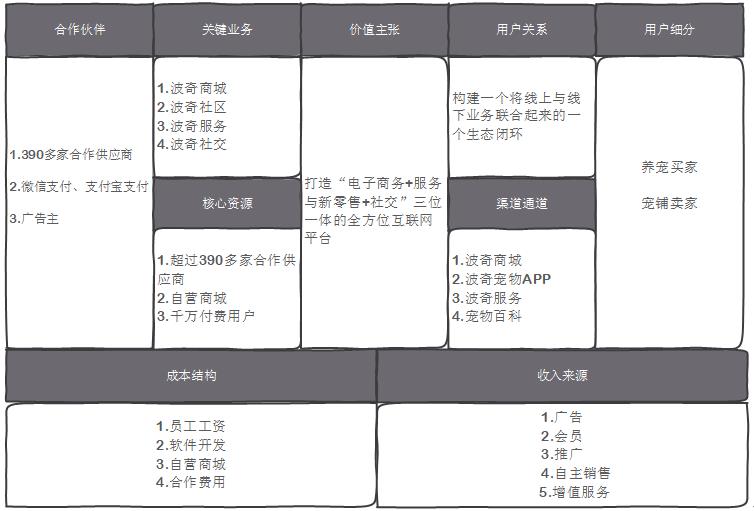
Figure 311 Boqi Pet APP Business Model Canvas
Boqi Pet is a self-selling B2C mall. Users can buy not only the goods in the platform stores but also the goods in Boqi’s own mall after using this platform.
Boqi Pet strives to build an all-round Internet platform of "e-commerce+service and new retail+social interaction" with a brand-new concept of pet rearing, and at the same time, it aims at traffic, brand promotion and user education.
A. Flow
Boqi is a platform for selling things, which is its commercial nature. Boqi can help brands sell more efficiently.
B. Brand promotion
Boqi is also a platform for brand promotion. There are actually a lot of advertising spaces in JD.COM and Tmall, including its own platform, which can help brand promotion.
C. User education
Pochi is unique in user education. Boqi not only sells things, but also helps good pet brands and does a lot of popularization and education work for users.
Through the channels of Boqi Mall, Boqi Pet APP, Boqi Service and Boqi Encyclopedia, users will be built into an ecological closed loop that combines online and offline services.
Boqi Pet has more than 390 cooperative suppliers and self-operated shopping malls. In terms of shopping malls, communities, services and social activities, it has benefited from advertisers, membership, store promotion, independent sales and value-added services (warehousing and logistics construction, online agency operation, etc.).
3) Product function
A. Information architecture
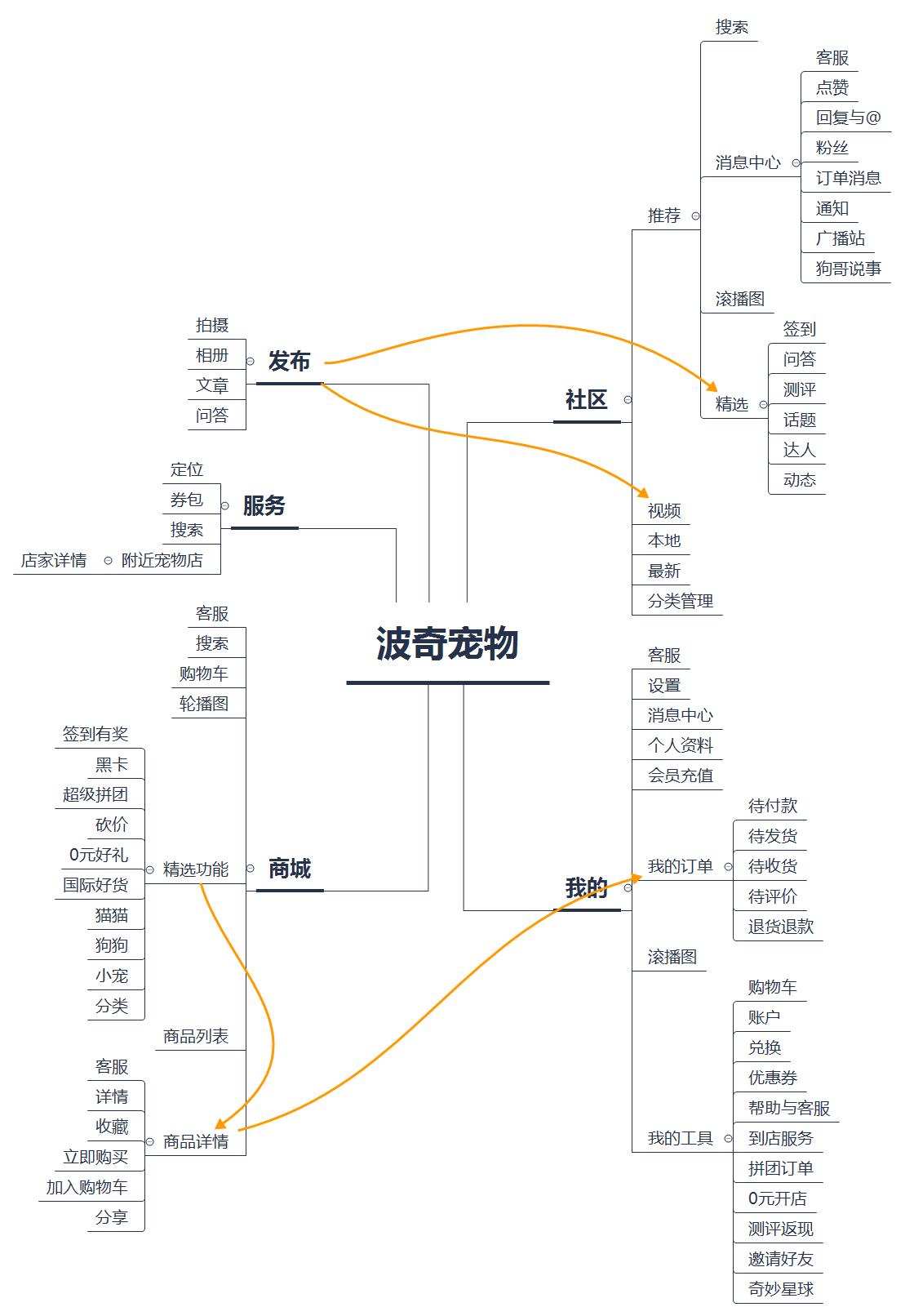
Figure 312 Boqi Pet APP Information Architecture
Boqi pets are mainly divided into five parts: shopping mall, community, release, service and mine. It can also be seen that Boqi Pet has built an all-round Internet platform of "community+e-commerce+service", giving users a different shopping experience.
By increasing the production platform of pet content in the community, Boqi Pet enriches the shopping experience of users, and on the other hand, the promotion of weak social mode is also a channel to obtain customers. The new pet e-commerce model of Boqi Pet can not only increase the stay time of users using products, but also bring transformation; At the same time, it is also a means to increase and retain users.
B. Process logic
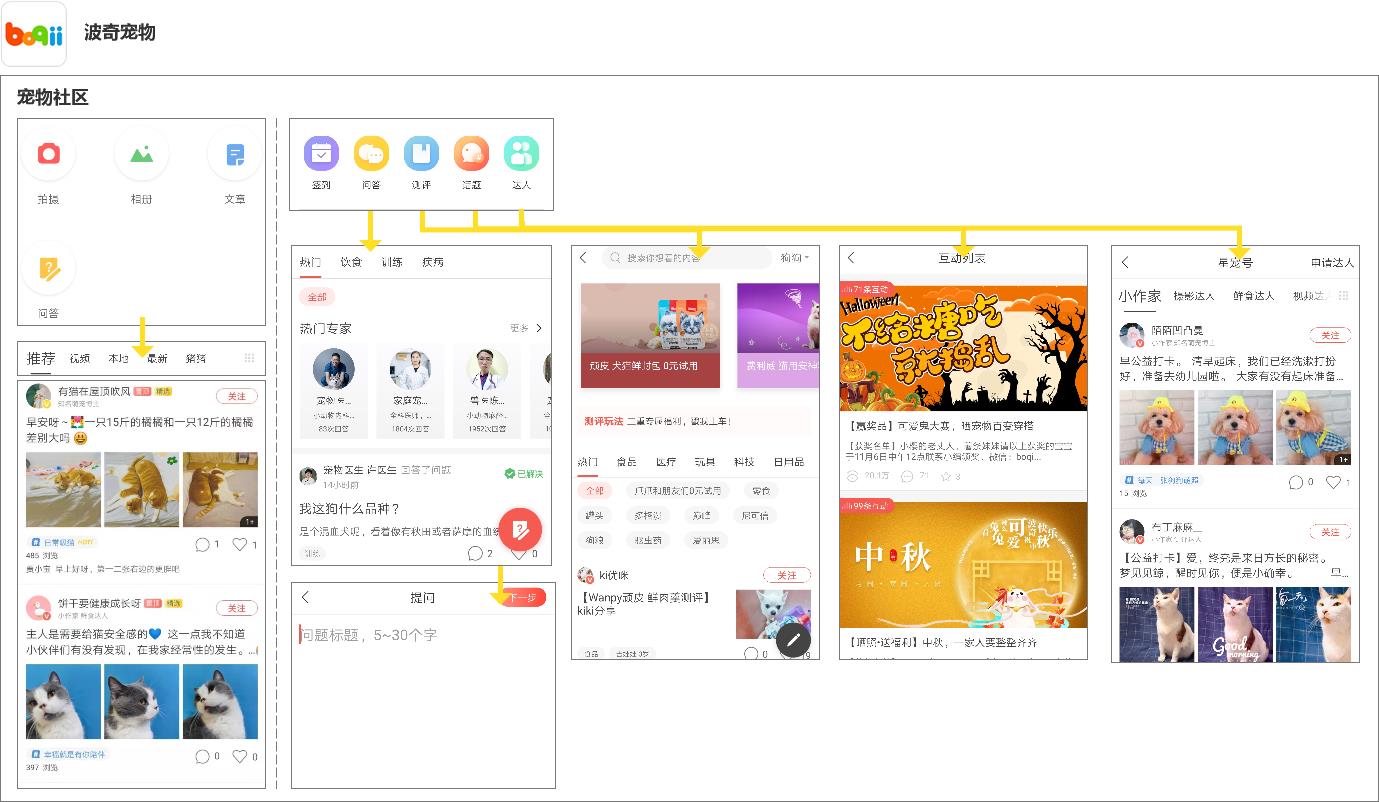
Figure 313 Page Flow of Boqi Pet APP Community
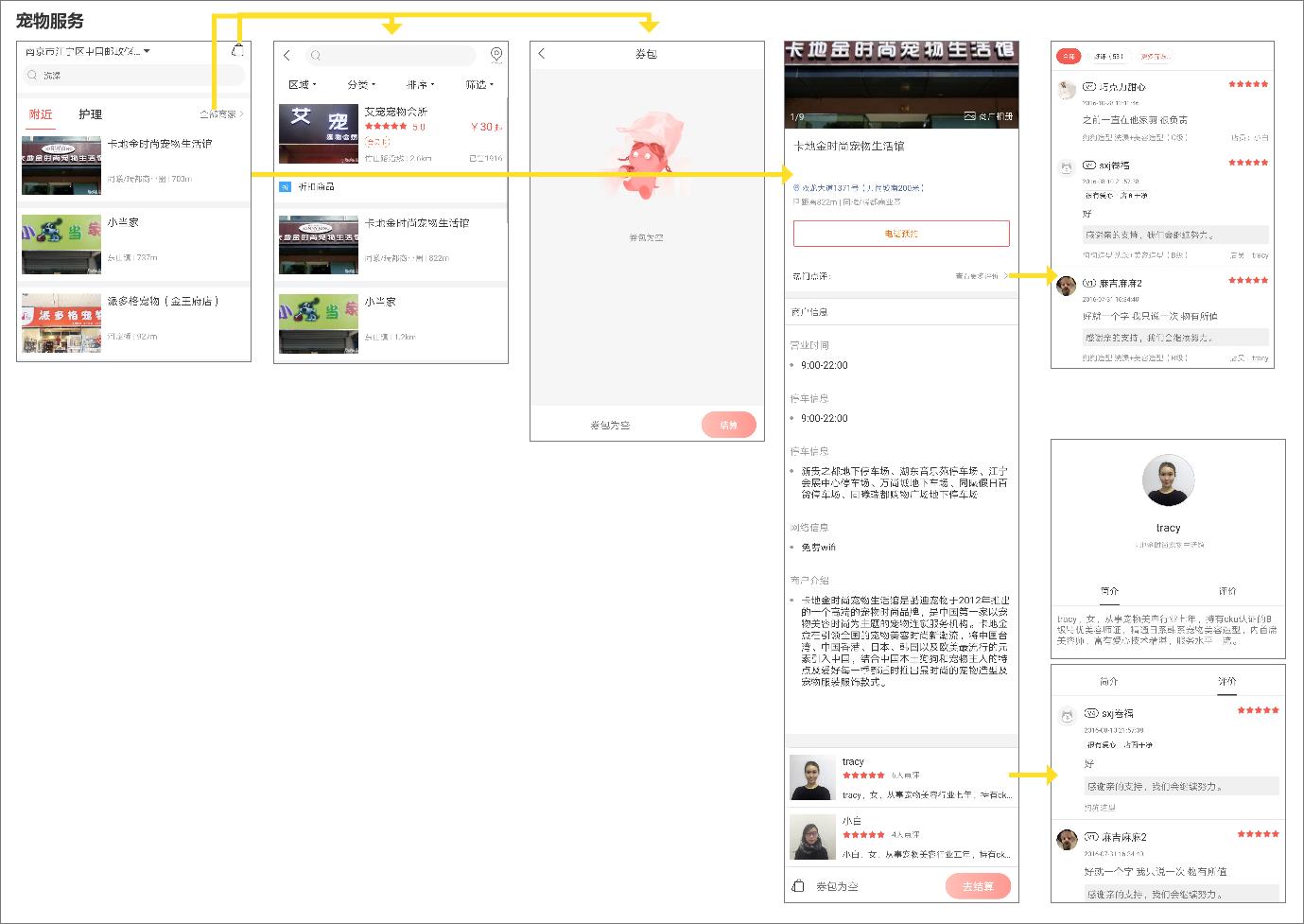
Figure 314 Page Flow of Boqi Pet APP Service
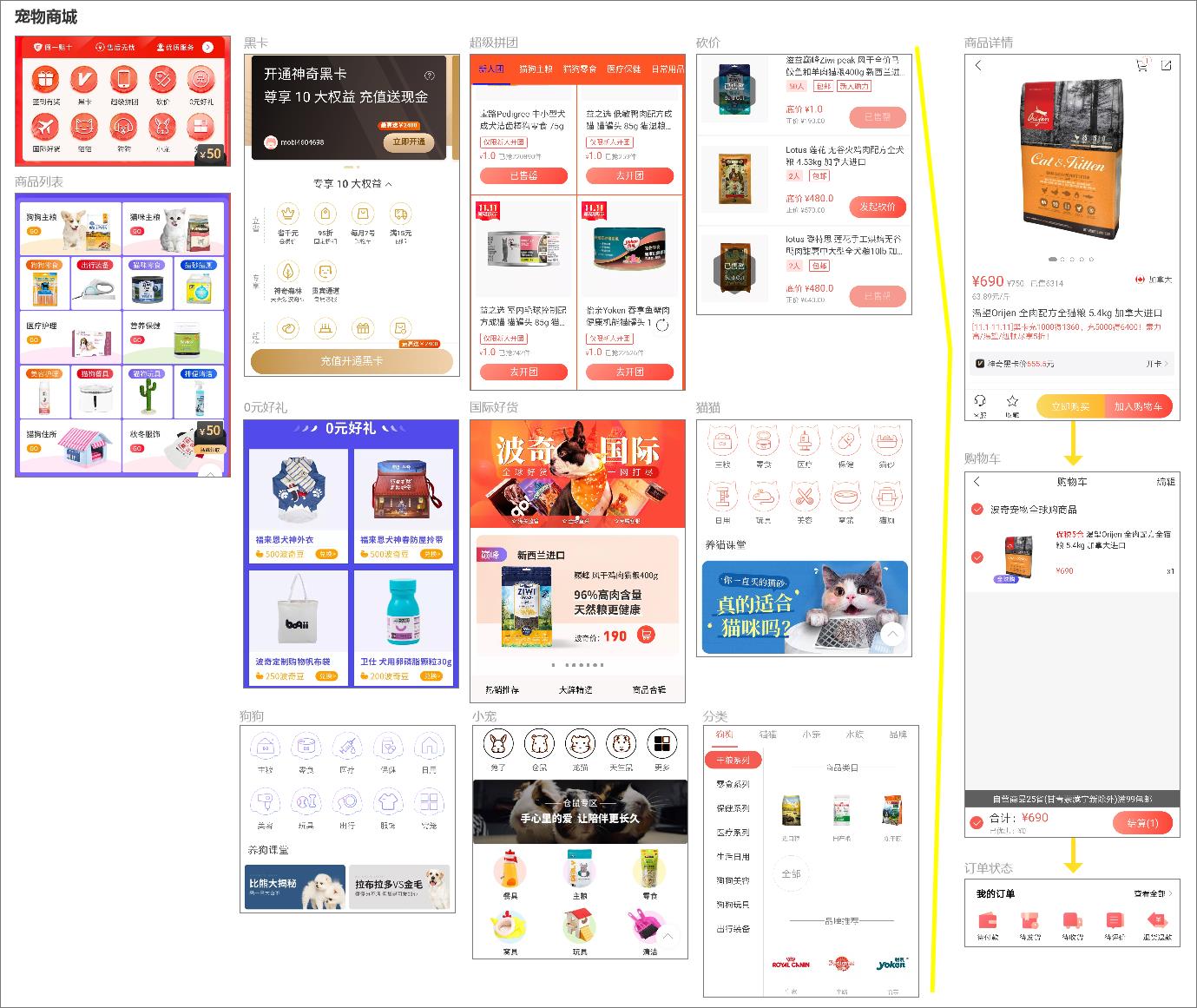
Figure 315 Page Flow of Boqi Pet APP Mall
Here, the logical flow of Boqi pet products is analyzed from three aspects (community/socialization, service and shopping mall).
- In the social aspect (as shown in Figure 3-13), users can view the photo albums/videos/articles published by other talents on the homepage and can comment/like/pay attention to support talents; In the community, there are four parts: question and answer, evaluation, topic and talent. Users can also interact with other users by posting photos/videos/articles/questions and answers.
- In terms of service (as shown in Figure 3-14), Boqi Pet has reached cooperation with pet shops in various regions, and can directly find the favorite stores on it. Click on a selected store to view its detailed information (including name, location, telephone reservation, popular comments, business hours, parking time, parking information, network information, merchant introduction, detailed introduction of pet service personnel and other people’s evaluation), and at the same time, it can settle the store service on the mobile phone.
- In terms of shopping malls (as shown in Figure 3-15), the selected categories include black cards, over-value groups, bargaining, 0 yuan gifts, international good goods, cats, dogs, small pets and fine classification. Each activity form has different preferential ways and purchasing strategies. In addition, there are newcomers’ exclusive, pre-sale venue, spike today, over-value group purchase, limited-time snapping, must-buy list, big-name venue, ace explosion, direct category and guessing that you like to view different products from different angles. When users enter the details page of a product, they will be faced with the choice of buying it immediately or joining the shopping cart. At this time, the specific operation process of the product is shown in Figure 3-16 below.
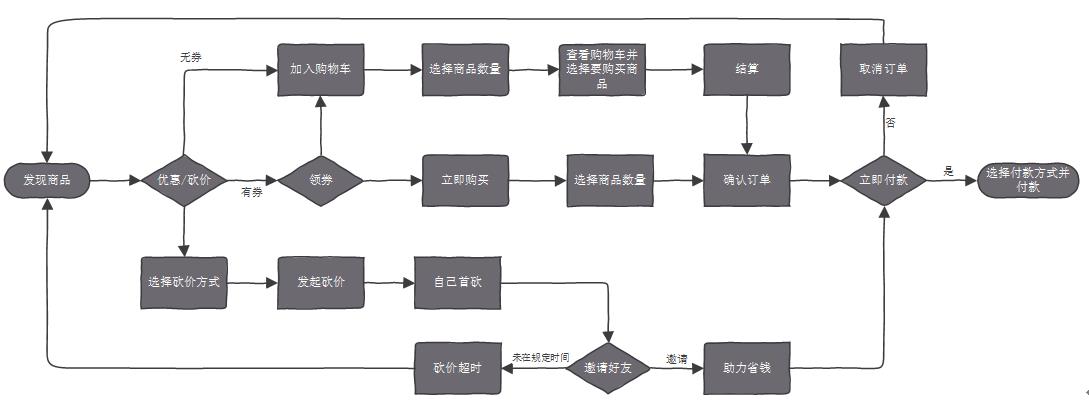
Figure 316 Boqi Pet APP Purchase Process
4) Operation strategy
A. Operating mode
- Membership system: there are two levels of membership system for Pochi pets, one is magic card, and the other is magic black card. Magic card enjoys four major rights and interests of members: membership price, fixed discount, exclusive shopping festival and birthday privilege, while magic black card enjoys ten major rights and interests of members: membership price (which will be more favorable than magic card, and there are very few cases with the same price), fixed discount, exclusive shopping festival, birthday privilege, wave beans (200 per month), over 15 packages of postage, gift sharing coupons, exclusive customer service and pre-sale.
- Coupons: exclusive for newcomers, full reduction, and redemption codes for coupons.
- Evaluation cashback: users get the corresponding income by writing articles about testing goods, and users who become experts in evaluation will get higher income. In addition, users who join magic cards or magic black cards will get 1~2% higher cashback of evaluation income than ordinary users.
- Inviting friends: After successful registration, the invited friends will get the 270 yuan Newcomer Gift Package, and at the same time, they will get 15% of the actual amount paid by their friends as a bonus. The amount of the bonus can be withdrawn when it exceeds that of 10 yuan, and the accumulated amount exceeds that of 100 yuan convertible goods.
- Virtual game: magic forest, the exclusive value-added benefits of members of magic black card, and the extra gains that magic black card users can get by recharging their cards (real-time recharging) during the validity period of rights and interests. The harvest result is Poqi beans, which can be used in Poqi Mall. Magic planet, after users enter the activity, they will get magic seeds to upgrade and grow by watering energy. When the seed grows to the 6th level, it will grow a piece of Jin Yezi to receive, and you can choose convertible goods for free when you use Jin Yezi. You can get an extra piece of Jin Yezi when you complete the task of inviting five new users, and you can redeem two prizes.
B. Version iteration
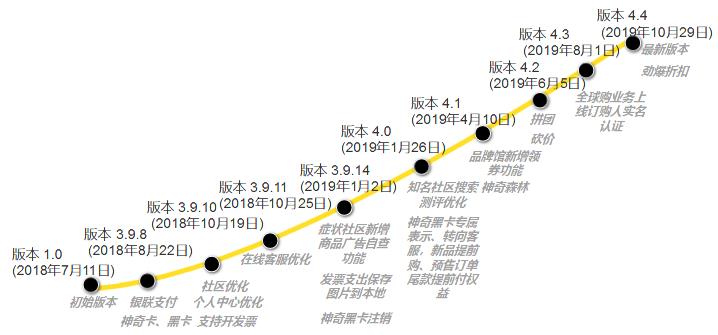
Figure 317 iteration of Boqi pet APP version
According to APPannie, Boqi Pet App was first released on July 11th, 2018, and updated with a new version every week on average. As can be seen from Figure 3-17 above, while consolidating the mall business, Boqi Pet has not slackened off its community business at all, which shows that Boqi Pet wants to develop in a coordinated way in terms of weak social interaction and strong business.
Of course, the rapid development of Boqi pet is inseparable from its social efforts, and the company’s influence is enhanced by increasing cumulative users, thus increasing revenue.
Therefore, it can be predicted that Pochi can also strengthen related businesses:
C. Pay attention to private chat
By adding private chat function, the interaction between users can be improved.
D. Strengthen the private customization of black card members
At present, in addition to the benefits of ordinary commodity concessions, the private subscription enjoyed by black cards also has exclusive customer service. If you upgrade to black card butler service on this basis, you can increase the desire of users to recharge black cards. The service content can include professional evaluation of users’ pets, designation of diet plan, medical plan, birth plan, exercise plan, pet dynamic popularity and so on.
E. live broadcast
By increasing the live broadcast function, the number of user downloads is increased, the interaction between users is improved, and the user stickiness is improved.
F. Offline community activities
Pet exhibitions, pet public welfare activities, pet games and other forms enhance the pet community and enhance the brand of Boqi pets.
G. Other short video platforms
By creating official accounts of short videos such as Tik Tok, Watermelon, Aauto Quicker, etc., they can be used as content distribution channels for internal production of products, share short videos with pets as content, and promote user traffic acquisition of products.
5) Summary
In the Top 100 Unicorn Enterprises in China issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Boqii was mentioned, ranking 83rd, and it was the only company in the pet industry called Unicorn.
As a representative of many pet shopping malls, Boqi Pet has been developing in a trinity way of "e-commerce+service and new retail+socialization".
In the community, users have questions and answers, evaluation, topics and people to communicate; In the mall, users have a list of goods to choose from, as well as bargaining and other forms; In terms of service, Boqi Pet has connected more than 3,000 pet shops and pet hospitals, which not only provides convenience for users, but also brings customers to many stores. At the same time, Boqi Pet has built several warehouses to provide goods.
Boqi Pet has also made great efforts in its operation, and improved its operation from the strategies of membership, discount, cash back, inviting friends and virtual games. Now Boqi Pet should strengthen its brand influence to gain more users and maintain its dominant position in the pet industry.
The above is the whole content of "Analysis of 68 Pet Apps (Part I)", and the rest will be published in time.
I was engaged in Java development before, and I didn’t enter the product for long. At the same time, I am now "looking for a new job opportunity". I am currently in Nanjing, but I may go to Beijing after the year.
Finally, if you have any suggestions for this article, please leave a message or exchange private messages below.
Above.
This article was originally published by @ Xiaoqi. Everyone is a product manager. It is forbidden to reprint without permission.
The title map comes from Unsplash and is based on CC0 protocol.